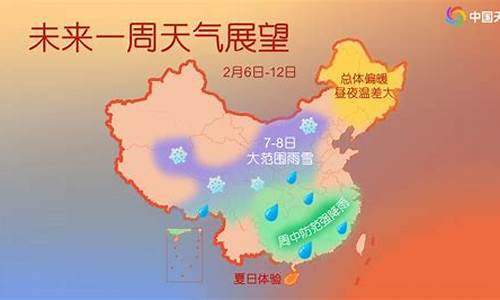
天气决定胜负英语_天气将对明天的足球比赛产生影响的英文
1.历史上由天气决定胜负的战争有哪些
2.表示天气的英语单词有哪些?
3.天气好转怎么说用英语

Weather affects all of us in one way or another, directly or indirectly. For example, good weather makes people happy. Bad weather makes people sick and depressed. Be sides, on a fine day, one can go out for a walk or play a game in the open. On a rainy day, however, he can only stay indoors, in a word, weather is part of life for all of us.
The first thing that many people do after getting up is to see what the weather is like. With a knowledge of the weather people can arrange work and life of the day. If it is fine, he may decide to go on a picnic. If it is cloudy, he will have to take a raincoat or an umbrella with him when he is leaving the house. Whatever the weather may be, one tends to adjust his activities to it accordingly.
In order to know what the weather will he, special people are hired 1o provide this information. They collect data, analyze them and predict the weather of the coming day. This information, which is announced on the radio or on TV, is usually very accurate. Thanks to the efforts of those professionals, we can always know the weather in advance and get prepared for it.
历史上由天气决定胜负的战争有哪些
The weather is a set of all the phenomena in a given atmosphere at a given time.It also includes interactions with the hydrosphere.The term usually refers to the activity of these phenomena over short periods (hours or days),as opposed to the term climate,which refers to the average atmospheric conditions over longer periods of time.When used without qualification,"weather" is understood to be the weather of Earth.Weather most often results from temperature differences from one place to another.On large scales,temperature differences occur because areas closer to the equator receive more energy per unit area from the Sun than do regions closer to the poles.On local scales,temperature differences can occur because different surfaces (such as oceans,forests,ice sheets,or man-made objects) have differing physical characteristics such as reflectivity,roughness,or moisture content.Surface temperature differences in turn cause pressure differences.A hot surface heats the air above it and the air expands,lowering the air pressure.The resulting horizontal pressure gradient accelerates the air from high to low pressure,creating wind,and Earth's rotation then causes curvature of the flow via the Coriolis effect.The simple systems thus formed can then display emergent behaviour to produce more complex systems and thus other weather phenomena.Large scale examples include the Hadley cell while a smaller scale example would be coastal breezes.The strong temperature contrast between polar and tropical air gives rise to the jet stream.Most weather systems in the mid-latitudes are caused by instabilities of the jet stream flow (see baroclinity).Weather systems in the tropics are caused by different processes,such as monsoons or organized thunderstorm systems.Because the Earth's axis is tilted relative to its orbital plane,sunlight is incident at different angles at different times of the year.In June the Northern Hemisphere is tilted towards the sun,so at any given Northern Hemisphere latitude sunlight falls more directly on that spot than in December (see Effect of sun angle on climate).This effect causes seasons.Over thousands to hundreds of thousands of years,changes in Earth's orbital parameters affect the amount and distribution of solar energy received by the Earth and influence long-term climate (see Milankovitch cycles).On Earth,common weather phenomena include such things as wind,cloud,rain,snow,fog and dust storms.Less common events include natural disasters such as tornadoes,hurricanes and ice storms.Almost all familiar weather phenomena occur in the troposphere (the lower part of the atmosphere).Weather does occur in the stratosphere and can affect weather lower down in the troposphere,but the exact mechanisms are poorly understood.[1] The atmosphere is a chaotic system,so small changes to one part of the system can grow to have large effects on the system as a whole.This makes it difficult to accurately predict weather more than a few days in advance,though weather forecasters are continually working to extend this limit through the scientific study of weather,meteorology.It is theoretically impossible to make useful day-to-day predictions more than about two weeks ahead,imposing an upper limit to potential for improved prediction skill.[1] Chaos theory says that the slightest variation in the motion of the ground can grow with time.This idea is sometimes called the butterfly effect,from the idea that the motions caused by the flapping wings of a butterfly eventually could produce marked changes in the state of the atmosphere.Because of this sensitivity to small changes it will never be possible to make perfect forecasts,although there still is much potential for improvement.The sun and oceans can also affect the weather of land.If the sun heats up ocean waters for a period of time,water can evaporate.Once evaporated into the air,the moisture can spread throughout nearby land,thus making it cooler.
表示天气的英语单词有哪些?
楼主!!我对此略有了解!如能帮到你,请速采纳!!!
1.兵败铁滑卢
大雨倾盆,道路泥泞,错失战机!!
2.昆阳之战
大风大雨 王莽的虎豹大军覆灭
史书记载“屋瓦皆飞,雨下如注,虎豹皆股战,(王莽)士卒赴水溺死者以万数”
3.鹿耳门之战
借助涨潮 郑成功收复台湾
4.西班牙无敌舰队覆灭
毁于台风
西班牙皇帝嚎啕大哭:“我是让他同英军作战,不是和惊涛骇浪搏斗”。
5.台风战役
德军发动的台风战役
就是莫斯科保卫战,冰天雪地,德军败退
6.诺曼底登陆
借助好天气!
当时德军西线司令隆美尔对部下说:“天气恶劣,可以考虑休整一下”。
德军放松戒备,甚至连一些理性的巡逻都取消了。盟军突袭,一举成功!
7.元朝远征日本
两次因台风失败!日本认为是神仙相助,这就是日本神风的由来!!
8.赤壁之战
万事具备,只欠东风!
9.李朔雪夜袭蔡州
利用大雪 扮羊突袭
10.白登之围
借助大雾,刘邦逃脱
11.美国独立战争中长岛战役
借助大雾,华盛顿逃脱,否则很可能全军覆没
美国都没了
楼主你可满意?字字手打,请速采纳
天气好转怎么说用英语
表示天气的英语单词有:
1、snowy
adj.多雪的,下雪的;雪白的;白雪覆盖的
2、storm
n.暴风雨,暴风雪,风暴;(感情或反应的)爆发,迸发;强低气压天气,旋风;暴雨般的飞弹(或打击);(军队的)强击,猛攻
v.猛烈攻击,突然袭击
3、windy
adj.多风的,风大的;夸夸其谈的,空话连篇的;胃内气胀的;(道路,河流)蜿蜒的,弯弯曲曲的;(人)紧张的,忧虑的
4、sunny
adj.阳光充足的,(地方)暖和的;(人,性格)开朗的,阳光的
5、foggy
adj.有雾的,雾气茫茫的;迷糊的,朦胧的;模糊的,糊涂的
天气好转[网络] zhu n zhu n;[例句]除非天气好转,不然我们就不得不取消比赛了。Unless the weather improves, we will have to cancel the game
声明:本站所有文章资源内容,如无特殊说明或标注,均为采集网络资源。如若本站内容侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系本站删除。